Colossus Computer, Bletchley Park
Introduction
The photograph on this page of Colossus Computer, Bletchley Park by Gerald Massey as part of the Geograph project.
The Geograph project started in 2005 with the aim of publishing, organising and preserving representative images for every square kilometre of Great Britain, Ireland and the Isle of Man.
There are currently over 7.5m images from over 14,400 individuals and you can help contribute to the project by visiting https://www.geograph.org.uk
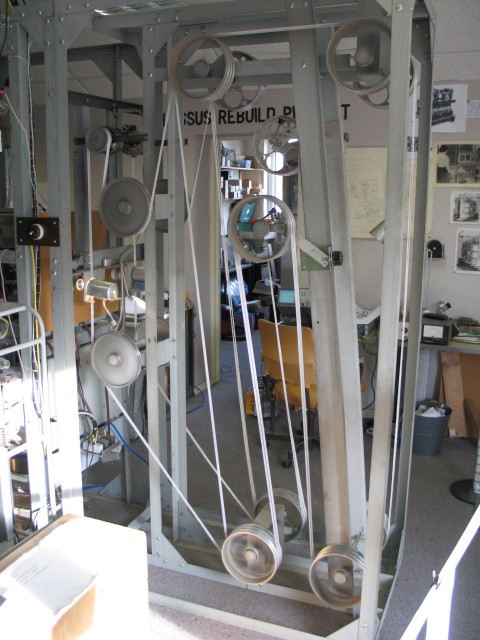
Image: © Gerald Massey Taken: 31 Oct 2009
The Colossus machines were electronic computing devices used by British codebreakers to read encrypted German wireless messages during World War II. The original machine was designed during 1943-4 by a team led by Tommy Flowers at the Post Office Research Station at Dollis Hill - the machine's Post Office roots are plainly evident in the Strowger-type relays, uniselectors and equipment racks that were then much in evidence in the UK's automatic telephone exchanges. Colossus machines (eventually there were ten in all) were the world's first programmable, digital, electronic, computing devices. They used thermionic valves (vacuum tubes), the fastest switching devices then available, to perform calculations aimed at deciphering German wireless traffic that was encrypted using the Lorenz SZ40/42 machine. In the absence of magnetic disc or semi-conductor technology, encrypted messages were read by Colossus at high speed using punched paper tape for storage and an optical reader. Following the end of WWII., most of the machines were taken apart and their components recycled, but two survived at GCHQ Cheltenham where they were used for various purposes until 1960. The fully-functional replica of a Colossus Mark 2, shown here and now on display at the National Museum of Computing (in H Block) Bletchley Park, was reconstructed by a team under the direction of Tony Sale, and completed in November 2007. For more detailed information on Colossus, see . . . . http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Colossus_computer This view is of the machine's paper tape storage device. The tape is the thin white ribbon, which forms a continuous loop moving at high speed over an optical reader. The tape holds teleprinter code (rows of punched holes read by the optical reader) representing the massage being de-ciphered. For other views of Colossus, see: Image; Image; Image; Image; Image; Image; Image; Image; Image; Image; Image; Image See also . . . . Image and Image

